Your cart is currently empty!
Category: Teachers & Parents
Information and educational materials in teaching kids about nature and trees for teachers and parents resources.
-
Native Trees of Indiana

Sandy gets up close to view trees! Sandy loves the diversity of trees that are native to Indiana! Whenever she gets a chance, she puts on her safety equipment and goes out with her fellow Arbor Rangers ™ to view and climb trees.
Trees come in all shapes and sizes and Indiana, for example, has over 100 native species!
Did you know that some of these Indiana tree species are in common with nearby states?
For instance, the Indiana State Tree, the Tulip Tree (also known as Yellow Poplar; scientific name, Liriodendron tulipifera), is also the State Tree of Kentucky and Tennessee! It is native from Connecticut and southern New York, westward to southern Ontario and northern Ohio, and south to Louisiana and northern Florida.
The most common types of trees in Indiana range from:
- CONIFER (a.k.a. EVERGREEN or Softwood) trees bear cones with embedded seeds and have needle-like or scale-like leaves that remain “ever” green throughout the year. Because these plants do not produce flowers, they are among the group of plants known as “Gymnosperms“.

Eastern White Pines (Pinus strobus) adorn a front yard in this neighborhood. - DECIDUOUS HARDWOOD (a.k.a. Broadleafed) trees which are trees with broader, flattened, “fan-like” leaves (simple or compound of various shapes and sizes). These are seed-producing plants, like conifers, but they differ because they bear flowers (some more distinctly than others) and thereby are among a larger diverse group of plants called “Angiosperms“. Most species’ leaves will change color before dropping off in the fall season. This is true in other cooler climate states, but rarer in warmer or tropical climate states.

Sugar Maples (Acer saccharum) brighten up a neighborhood in fall! - DECIDUOUS EVERGREEN trees which look like typical conifers, but surprisingly lose their foliage in the fall just like deciduous hardwood trees! These are also among the group of plants known as “Gymnosperms“.

Baldcypress (Taxodium distichum) by the canal have lost their summer foliage. Do Your TREE-Search!
Sandy has helped put together the following list of trees that are native to Indiana. Included are non-native, INVASIVE SPECIES.* This is a searchable & sortable list of conifers and hardwood trees featuring their Scientific Names as well as Common Names by which they are generally known and includes links to more tree information** by clicking on their Scientific and Common Names.
DEFINITIONS The list also reflects some quick tree facts, such as:
- Type: One of the three tree types: Conifer, Deciduous Hardwood, or Deciduous Evergreen.
- Leaf: The general type of leaf form.
- Simple – a single leaf blade joined by its stalk (or petiole) to a woody stem.
- Compound – a leaf that is itself composed of more than one leaflet and these leaflets are attached to its single leaf stalk.
- Needle-like – slender, sharp-pointed leaf.
- Scale-like – leaves with short overlapping segments.
- Branching: Briefly describes the general, characteristic, growth structure of the plant’s stems/branches.
- Alternate – branching that is staggered or not directly across from one another.
- Opposite – branches that are directly across from each other.
- Height: The approximate average maximum height the tree species may obtain at maturity.
- Spread: The approximate average maximum width the tree species may obtain at maturity.
- Fall Color: The general color of the foliage during the fall/winter season; leaves detach and drop from deciduous tree types. Find out Why Leaves Change Color.
- Hardiness Zones: Range of USDA Plant Hardiness Zones each plant has been reported to grow and usually thrive in. To learn more about hardiness zones, see our USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map – INDIANA page.
HINT: Viewing the list on a small screen mobile device in portrait position may not display all columns. Try viewing this page with your device in landscape orientation to broaden your view of all featured columns of the tree list.
Explore the Native Trees of Indiana
*An invasive species is defined as a species that is: 1) non-native (or alien) to the ecosystem under consideration and 2) whose introduction causes or is likely to cause economic or environmental harm or harm to human health. Invasive species that occur in urban forests should be removed, if and wherever possible, or at least avoid being planted or replanted.Scientific Name(s) Common Name(s) Type; Leaf; Branching Height Spread Fall Color Hardiness Zones PEST ALERT! Juniperus virginiana Redcedar, Eastern; Red Cedar, Eastern Conifer, Scale-like, Alternate 50′ 20′  Green
Green2-9 EGM (seldom attacked by EGM) Pinus banksiana Pine, Jack; Jack-pine Conifer, Needle-like, Alternate 40′ 18′  Green
Green3-7 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM, SLF) Pinus strobus Pine, Eastern White; Pine, White Conifer, Needle-like, Alternate 100′ 50′  Green
Green5-7 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM, SLF) Pinus virginiana Pine, Virginia; Virginia-pine; Scrub-pine Conifer, Needle-like, Alternate 50′ 20′  Green
Green4-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM, SLF) Thuja occidentalis Arborvitae, Eastern; White Cedar, Northern; White Cedar; Tree of Life Conifer, Scale-like, Alternate; Endangered 50′ 15′  Green
Green2-8 EGM (seldom attacked by EGM) Tsuga canadensis Hemlock, Eastern; Hemlock, Canadian Conifer, Needle-like, Alternate 90′ 40′  Green
Green4-7 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Larix laricina Larch, American; Larch, Eastern; Tamarack Evergreen, Deciduous, Needle-like, Alternate 75′ 30′  Yellow
Yellow2-8 EGM Taxodium distichum Baldcypress; Bald Cypress Evergreen, Deciduous, Needle-like, Alternate; Threatened 120′ 45′  Red, Copper
Red, Copper5-9 Acer negundo Boxelder; Maple, Ash-leaved Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 60′ 40′  Red-orange
Red-orange3-8 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by ALB) Acer nigrum Maple, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Opposite 80′ 60′  Yellow
Yellow4-8 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM, ALB) Acer platanoides Maple, Norway, incl. cultivar: Maple, Crimson King INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Opposite 80′ 40′  Yellow
Yellow4-8 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM, ALB) Acer rubrum Maple, Red Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Opposite 90′ 50′  Red-orange
Red-orange4-8 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM, ALB) Acer saccharinum Maple, Silver; Silver-maple Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Opposite 80′ 60′  Yellow
Yellow4-8 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM, ALB) Acer saccharum Maple, Sugar; Sugar-maple Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Opposite 80′ 60′  Yellow-orange
Yellow-orange4-8 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM, ALB) Aesculus flava (A. octandra) Buckeye, Yellow; Buckeye, Sweet Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 90′ 50′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown3-8 EGM, ALB (especially favored by ALB) Aesculus glabra Buckeye, Ohio Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 50′ 35′  Red-brown
Red-brown3-7 EGM, ALB (especially favored by ALB) Amelanchier arborea Serviceberrry, Downy; Serviceberry, Common Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 25′  Yellow-red
Yellow-red4-9 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Amelanchier laevis Serviceberry, Allegheny: Shadbush, Allegheny; Serviceberry, Smooth Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 10′  Yellow-red
Yellow-red4-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Asimina triloba Pawpaw Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 30′  Yellow
Yellow5-8 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Betula alleghaniensis Birch, Yellow Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 60′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Betula nigra Birch, River; Birch, Red Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 60′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Betula papyrifera Birch, Paper; Birch, White Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 50′ 60′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Betula populifolia Birch, Gray; Birch, Grey Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate; Presumed Extirpated 30′ 20′  Yellow
Yellow4-6 EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Carpinus caroliniana Hornbeam, American; Beech, Blue; Musclewood; Beech, Water Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 25′  Yellow-red
Yellow-red3-9 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Carya cordiformis Hickory, Bitternut; Bitternut-hickory Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 80′ 50′  Yellow
Yellow3-7 Carya glabra Hickory, Pignut; Pignut-hickory Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 60′ 40′  Yellow
Yellow5-9 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Carya illinoinensis Pecan Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 100′ 75′  Yellow
Yellow6-9 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Carya laciniosa Hickory, Shellbark; Shellbark-hickory Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 120′ 60′  Yellow
Yellow5-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Carya ovalis Hickory, Red; Red-hickory; Hickory, Sweet Pignut; Sweet Pignut-hickory Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 80′ 80′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown4-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Carya ovata Hickory, Shagbark; Shagbark-hickory Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 80′ 40′  Yellow
Yellow4-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Carya pallida Hickory, Sand; Hickory, Pale Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate; Threatened 40′ 43′  Yellow, Pale
Yellow, Pale5-9 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Carya texana Hickory, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate; Endangered 50′ 43′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown5-9 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Carya tomentosa Hickory, Mockernut Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 60′ 30′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown6-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Castenea dentata Chestnut, American Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate; Endangered 75′ 75′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown5-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Catalpa speciosa Catalpa, Northern; Catalpa Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Whorled 60′ 40′  Yellow-green
Yellow-green4-9 EGM (seldom attacked by EGM) Celtis laevigata Sugarberry; Hackberry, Southern Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 80′  Yellow
Yellow6-9 Celtis occidentalis Hackberry, Common; Hackberry, Northern Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 90′ 60′  Yellow
Yellow2-9 EGM, ALB (especially favored by EGM) Cercis canadensis Redbud; Redbud, Eastern Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 35′  Yellow
Yellow4-9 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Cladrastis kentukea (C. lutea) Yellowwood; Yellowwood, American; Yellowwood, Kentucky Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate; Threatened 60′ 55′  Yellow
Yellow4-8 Cornus alternifolia Dogwood, Pagoda; Pagoda-dogwood; Dogwood, Alternate-leaved Hardwood, Deciduous (Shrubby), Simple, Alternate 30′ 30′  Red, Purple
Red, Purple4-7 EGM, SLF (especially favored by SLF) Cornus florida Dogwood, Flowering Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Opposite 40′ 20′  Red, Rust
Red, Rust5-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by SLF) Crataegus crus-galli Hawthorn, Cockspur; Cockspur-thorn Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 25′ 25′  Orange-red
Orange-red3-7 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Crataegus mollis Hawthorn, Downy Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 25′ 30′  Orange-red
Orange-red3-6 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Crataegus punctata Hawthorn, Dotted Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 30′  Orange-red
Orange-red4-8 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Crataegus viridis Hawthorn, Green Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate; Threatened 25′ 25′  Red-orange
Red-orange5-7 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Diospyros virginiana Persimmon; Persimmon, Common Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 35′  Orange-red
Orange-red4-8 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Fagus grandifolia Beech, American Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 80′  Orange-red
Orange-red4-8 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM, SLF) Fraxinus americana Ash, White; Purple Ash Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 100′ 70′  Red, Purple
Red, Purple3-9 EAB, EGM, ALB, SLF (less preferred by EAB, ALB; seldom attacked by EGM;especially favored by SLF) Fraxinus nigra Ash, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 60′ 70′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 EAB, EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EAB; less preferred by ALB; seldom attacked by EGM) Fraxinus pennsylvanica Ash, Green; Ash, Red Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 50′ 70′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 EAB, EGM, ALB, SLF (especially favored by EAB, ALB; seldom attacked by EGM) Fraxinus profunda Ash, Pumpkin; Pumpkin-ash Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 60′ 70′  Red, Purple
Red, Purple5-9 EAB, EGM, ALB, SLF (seldom attacked by EGM) Fraxinus quadrangulata Ash, Blue Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 70′ 70′  Yellow, Pale
Yellow, Pale3-9 EAB, EGM, ALB, SLF (less preferred by EAB; seldom attacked by EGM) Gleditsia aquatica Waterlocust; Water-locust Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate; Endangered 60′ 39′  Yellow
Yellow6-9 Gleditsia triacanthos Honeylocust; Honey-locust Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 70′ 40′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown4-9 EGM (seldom attacked by EGM) Gymnocladus dioicus Kentucky Coffeetree; Kentucky Coffee-tree Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 100′ 50′  Yellow
Yellow3-8 Juglans cinerea Butternut; Walnut, White Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 60′ 50′  Yellow
Yellow3-7 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM) Juglans nigra Walnut, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 80′ 70′  Yellow
Yellow4-9 EGM, SLF (especially favored by EGM, SLF) Liquidambar styraciflua Sweetgum; Gum, Sweet; Gum, Red Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 120′ 50′  Orange-red
Orange-red5-9 EGM (especially favored by EGM) Liriodendron tulipifera Tuliptree; Tulip-tree; Poplar, Tulip; Poplar, Yellow Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 175′ 50′  Yellow
Yellow5-9 EGM, SLF (seldom attacked by EGM; especially favored by SLF) Magnolia acuminata Magnolia, Cucumber; Cucumber-tree; Cucumbertree Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate; Endangered 100′ 35′  Yellow, Gold
Yellow, Gold3-8 EGM Magnolia tripetala Magnolia, Umbrella; Umbrella-tree Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate; Endangered 20′ 30′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown5-8 Malus coronaria
(Pyrus coronaria)Crabapple, American; Crabapple, Wild; Crabapple, Wild Sweet; Crabapple, Sweet Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 25′  Yellow-green
Yellow-green4-8 Malus ioensis Crabapple, Prairie Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 25′ 25′  Red-orange
Red-orange4-8 Morus alba Mulberry, White; Mulberry, Silkworm INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 50′  Yellow
Yellow4-8 Morus rubra Mulberry, Red Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 70′ 35′  Yellow
Yellow5-10 Nyssa sylvatica Gum, Black; Gum, Sour; Tupelo, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 30′  Red, Copper
Red, Copper3-9 Ostrya virginiana Hophornbeam; Hop-hornbeam, American; Hop-hornbeam, Eastern; Ironwood Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 30′ 30′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 Oxydendrum arboreum Sourwood Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate; Threatened 60′ 25′  Orange-red
Orange-red5-9 Platanus occidentalis Sycamore; Sycamore, American Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 100′ 100′  Yellow
Yellow4-9 Populus balsamifera Poplar, Balsam; Balsam-poplar Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate; Presumed Extirpated 70′ 10′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 Populus deltoides Cottonwood; Cottonwood, Eastern Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 100′ 75′  Yellow
Yellow2-9 Populus grandidentata Aspen, Bigtooth; Aspen, Big-toothed; Aspen, Large-toothed Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 50′ 28′  Yellow, Gold
Yellow, Gold3-5 Populus heterophylla Cottonwood, Swamp Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 70′ 40′  Yellow
Yellow3-8 Populus tremuloides Aspen, Quaking; Aspen, Trembling Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 50′ 30′  Yellow
Yellow2-5 Prunus americana Plum, American; Plum, American Wild Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 25′ 25′  Orange-red
Orange-red3-10 Prunus hortulana Plum, Hortulan; Plum, Wild Goose Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 15′ 15′  Orange-red
Orange-red5-9 Prunus nigra Plum, Canada; Canada-plum Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 25′ 15′  Red, Purple
Red, Purple3-6 Prunus pensylvanica Cherry, Pin; Pin-cherry; Cherry, Fire Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 40′ 30′  Orange-red
Orange-red3-8 Prunus serotina Cherry, Wild Black; Cherry, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 25′  Yellow
Yellow3-10 Pyrus calleryana Pear, Callery, incl. cultivar: Pear, Bradford INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 50′ 35′  Red, Purple
Red, Purple4-9 Quercus acutissima Oak, Sawtooth INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 60′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown5-9 Quercus alba Oak, White Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 150′ 70′  Red
Red3-9 Quercus bicolor Oak, Swamp White Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 75′ 70′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown3-9 Quercus coccinea Oak, Scarlet Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 50′  Red, Deep
Red, Deep4-8 Quercus ellipsoidalis Oak, Northern Pin; Pin-oak, Northern; Oak, Hill’s Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 70′  Red, Rust
Red, Rust3-9 Quercus falcata Oak, Southern Red; Oak, Spanish Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 50′  Red, Copper
Red, Copper7-9 Quercus imbricaria Oak, Shingle; Shingle-oak Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 70′  Orange-red
Orange-red3-9 Quercus lyrata Oak, Overcup; Overcup-oak Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 60′  Orange-brown
Orange-brown6-9 Quercus macrocarpa Oak, Bur; Bur-oak; Oak, Mossycup Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 70′  Red, Copper
Red, Copper3-9 Quercus marilandica Oak, Blackjack; Oak, Black-jack Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 40′ 70′  Red
Red3-9 Quercus michauxii Oak, Swamp Chestnut; Chestnut-oak, Swamp Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 50′  Red
Red6-9 Quercus montana (Q. prinus) Oak, Chestnut; Oak, Rock Chestnut; Chestnut-oak, Rock; Oak, Rock; Oak, Mountain Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 75′ 60′  Yellow, Brown
Yellow, Brown5-9 Quercus muehlenbergii Oak, Chinkapin; Oak, Chinquapin; Chinkapin-oak; Oak, Yellow Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate; Endangered 80′ 70′  Orange-brown
Orange-brown3-9 Quercus pagoda Oak, Cherrybark; Cherrybark-oak Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 120′ 48′  Red, Copper
Red, Copper7-9 Quercus palustris Oak, Pin; Pin-oak Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 70′  Orange-red
Orange-red3-9 Quercus rubra Oak, Red; Oak, Northern Red Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 70′  Red, Deep
Red, Deep3-9 Quercus shumardii Oak, Shumard Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 60′  Orange-red
Orange-red5-9 Quercus stellata Oak, Post; Post-oak Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 50′ 70′  Red, Copper
Red, Copper3-9 Quercus velutina Oak, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 60′  Orange-red
Orange-red3-9 Robinia pseudoacacia Locust, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 80′ 35′  Yellow
Yellow4-8 Sassafras albidum Sassafras Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 90′ 40′  Red, Deep
Red, Deep5-9 Tilia americana Basswood, American; Linden, American Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 80′ 50′  Yellow
Yellow3-8 Ulmus alata Elm, Winged Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 50′ 40′  Yellow
Yellow6-9 Ulmus americana Elm, American Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 100′ 120′  Yellow
Yellow2-9 Ulmus pumila Elm, Siberian INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 50′  Yellow
Yellow5-9 Ulmus rubra Elm, Slippery; Elm, American Slippery Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 60′ 35′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 Ulmus thomasii Elm, Rock; Elm, Cork Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 90′ 90′  Yellow
Yellow3-7 Salix amigdaloides Willow, Peachleaf; Willow, Peach-leaf Hardwood, Deciduous (Shrubby), Simple, Alternate 40′ 17′  Yellow
Yellow2-8 Salix nigra Willow, Black Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 40′ 100′  Yellow
Yellow2-8 Aralia spinosa Devil’s Walkingstick; Devil’s-walkingstick; Hercules’ Club Hardwood, Deciduous (Shrubby), Compound, Alternate 20′ 10′  Red-orange
Red-orange4-9 Hamamelis virginiana Witch-hazel Hardwood, Deciduous (Shrubby), Simple, Alternate 20′ 25′  Yellow
Yellow3-8 Ptelea trifoliata Hoptree; Hoptree, Common; Hop-tree, Common; Wafer-ash Hardwood, Deciduous (Shrubby), Simple, Alternate 20′ 15′  Yellow
Yellow3-9 Rhus typhina Sumac, Staghorn; Staghorn-sumac Hardwood, Deciduous (Shrubby), Compound, Alternate 25′ 25′  Red-orange
Red-orange4-8 Sorbus decora Showy Mountainash; Showy Mountain-ash Hardwood, Deciduous (Shrubby), Compound, Alternate; Presumed Extirpated 30′ 70′  Red-orange
Red-orange3-9 Ailanthus altissima Tree of Heaven INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Alternate 70′ 50′  Yellow-green
Yellow-green5-8 Alnus glutinosa Alder, European Black; Alder, Black; Alder, Common INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Alternate 50′ 40′  Yellow-green
Yellow-green3-7 Paulownia tomentosa Princess Tree; Royal Paulownia; Empress Tree; Princesstree INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Simple, Opposite or Whorled 40′ 40′  Green
Green5-8 Phellodendron amurense Amur Cork Tree; Amur Corktree INVASIVE SPECIES Hardwood, Deciduous, Compound, Opposite 45′ 60′  Yellow
Yellow3-7
**Links for additional information include fact sheets from various federal and municipal entities and academic institutions. These fact sheets expand upon and feature a broader range of tree details, including identification photos. These factsheet links were specifically selected, based on the quality of their online content. We highly recommend the book “Native Trees of the Midwest“ by Sally Weeks (Purdue University). Please contact us regarding any broken web links.
[DISCLAIMER: Tree facts sometimes vary from source to source, and particularly from state to state. We conducted our research from multiple sources from within Indiana and then from states in our general region, with few exceptions. Arbor Rangers, LLC makes no guarantees, nor claims, as to fitness of the data represented other than that every attempt has been made to present such information as accurately as possible. After consulting the “101 Trees of Indiana” © 2003 publication as a basis for our tree list, we then cross-checked the information with other sources. Where sources differed in information, we gave preference to the data from the newer published book “Native Trees of the Midwest” (Revised and Expanded Second Edition) © 2010 and then, in the case where certain data was not cited in this publication, we used or averaged the data available from the other resources listed at the bottom of this page. This tree list is subject to modification without prior notification.]Native Trees of Indiana list compiled, created and copyright © 2017 Arbor Rangers, LLC.
Arbor Rangers, LLC would like to thank and acknowledge the following resources which made this compilation possible:
- Sally Weeks: “Native Trees of the Midwest“ (Second Edition) [ISBN 978-1-55753-572-6]
- Marion Jackson: “101 Trees of Indiana“ [ISBN 978-0-253-21694-6]
- Indiana University-Purdue University (Fort Wayne): Native Trees of Indiana River Walk website
- Elbert Little: “Field Guide to Trees: Eastern Region – North America“ [ISBN 0-394-50760-6]
- USDA Forest Service: “Silvics of North America“ (Agriculture Handbook 654) also their Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) and Fire Effects Information System (FEIS) online databases
- Butler University: Indiana Plant Atlas
- University of Florida Environmental Horticulture: 680 Tree Fact Sheets
- Missouri Botanical Garden: Plant Finder
- Ohio DNR Forestry: Common Ohio Trees
- Virginia Tech: Dendrology factsheets (“vTree” database)
- Arbor Day Foundation: Tree Identification
- The Morton Arboretum: Tree and plant descriptions
- Indiana Invasive Species Council: Official IISC Invasive Plant List
- Rebecca Weller’s: Trees For Me website
- University of Texas at Austin/Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center: Native Plant Finder
- Illinois Wildflowers: Trees, Shrubs, and Woody Vines of Illinois
- Minnesota Wildflowers: Trees in Minnesota
- New England Wild Flower Society/Go Botany: Woody Plants
- Friends of the Louisiana State Arboretum: Featured Species
- Global Species website
- Dave’s Garden website
- With special THANKS to Lindsey Purcell, Urban Forest Specialist, Purdue University for his expert review!
Find additional resources here on our TEACHER and PARENT RESOURCES page.
-
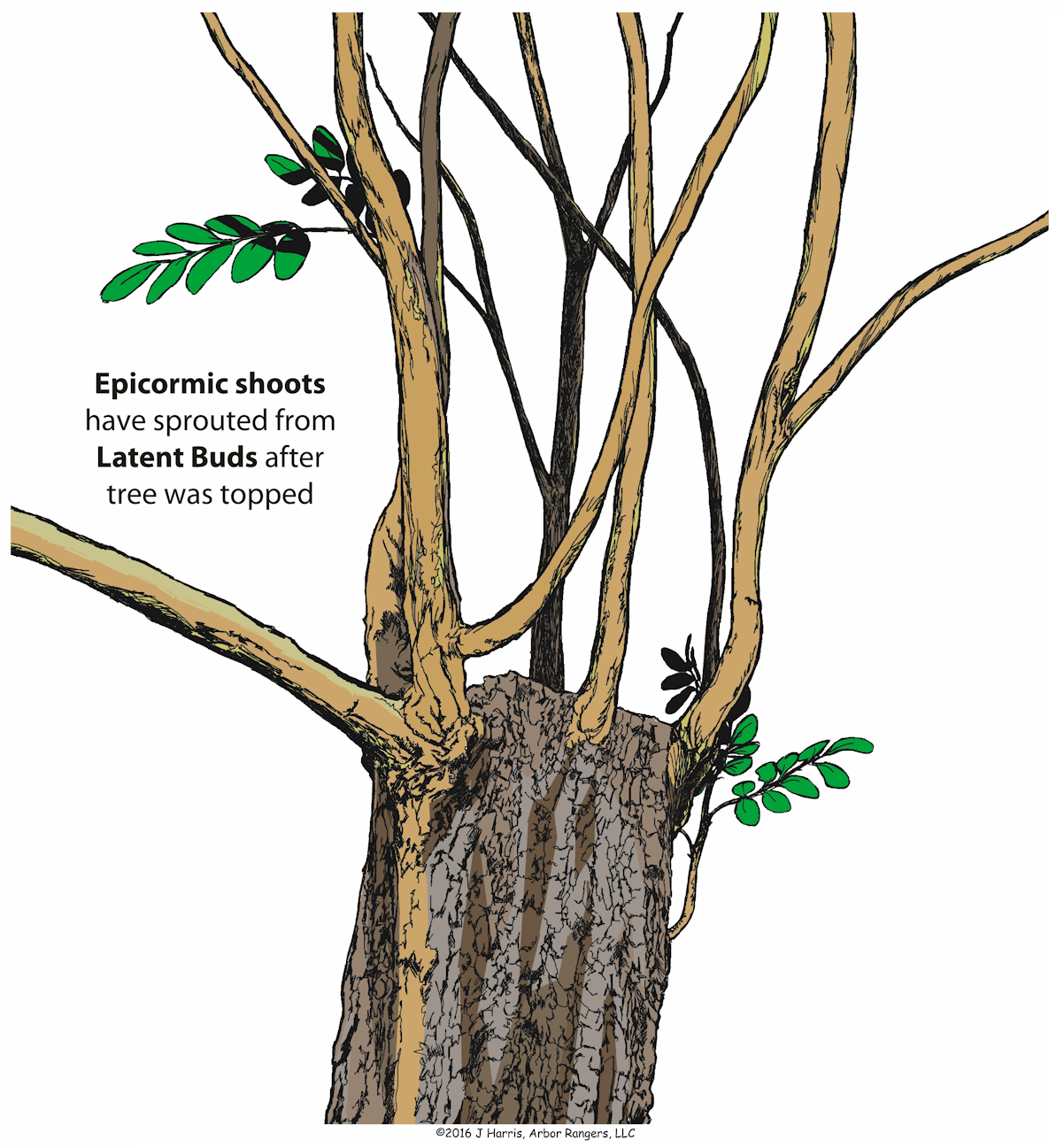
What Does a Tree Think of Pruning?
Guiding young and medium-aged trees to develop good branch architecture is key to sustainable tree plantings. The most common method of training and developing healthy growth is by means of proper pruning.
But, have you ever wondered how pruning affects a tree?
It’s not merely the removal of a broken or diseased or undesirable limb. Pruning not only changes a tree’s physical structure, for better or worse, but it also undergoes biological effects, which can have long-lasting affects on its future growth and development. Who knew, right?

We prune trees to remove broken or diseased or undesirable limbs, but have you ever wondered, “What do tree think?” Can pruning affect a tree biologically? What affect could Jeff’s pruning this tree (pictured above) have on its future growth and development? To learn more on how proper (or improper) pruning can impact your trees and when is the best time to prune, read the new publication: “Tree Pruning: What Do Trees Think?” (FNR-534-W Feburay 2017) by Lindsey Purcell (Urban Forestry Specialist, Purdue University).
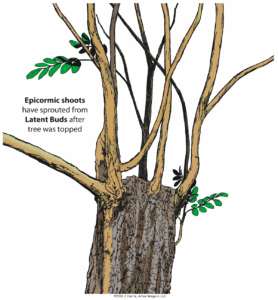
Epicormic shoots have developed from latent buds after this tree was topped. Topping trees is bad for a trees long-term health and not considered a proper pruning method. Be sure to also check out his related book “Tree Pruning Essentials“ (FNR-506-W July 2017).
-
Arbor Rangers ™ Puzzles & Activities Sheets
Arbor Rangers ™ “Brainy Series”™

The NEW Arbor Rangers™ “Brainy Series” Logo Do you like word search, maze, or picture puzzles? Download and print the latest Arbor Rangers ™ Puzzles & Activities Sheet!
- April 2016 AR “Brainy Series” promo booklet (Note: Combines previously released* activity sheet puzzles into a slightly newer format, with additional artwork and puzzles.)
- How to Draw Trees – The EASY Way!
Cross-WOODS Puzzle Solutions
*Archives:
- October 2015 AR Puzzles & Activities Sheet
- October 2014 AR Puzzles & Activities Sheet
- EAB Crossword Challenge
Ready for the puzzle solution? EAB Crossword Puzzle Answers
-

Indiana Natural Resources Teacher Institute
The Indiana Natural Resources Teacher Institute is a multi-day professional development workshop that will bring 18 teachers from across the state to Morgan-Monroe State Forest to see firsthand how forestry works in Indiana. Sessions include tours of public and private forest lands, forest industry facilities, and forestry research in Indiana.
The goal of the institute is to provide Indiana teachers with knowledge, skills and tools to effectively teach their students about forest ecology and forest management practices. The forest environment becomes the basis for integrating the learning of many subject areas, including environmental science, biology, natural resources, and social science. STEM concepts and principles will be incorporated throughout the sessions. The program empowers teachers to foster conceptual learning, critical thinking and decision-making skills in their classrooms.

Attendees are prepared for outdoor activities BENEFITS: The Natural Resources Teacher Institute emphasizes the importance of conservation of natural resources with special attention given to Indiana’s forests and forest products. The project-based approach integrates hands-on study of the natural and cultural resources of the local community, addresses concepts in ecology, sense of place, civics, economics and forest land management and stewardship. Participants will develop a curriculum project about forests or forestry for their classrooms. Participants will earn 30+ Professional Growth Points and receive a stipend upon documentation of implementing curriculum project. We link the concepts to the Indiana Learning Standards and provide training in Project Learning Tree materials.
WHEN AND WHERE: The Institute will begin on Monday, June 22 at 4:00 pm and conclude on Friday, June 26, 2015 at 12:00 pm. Our base of operation will be the Forestry Training Center at Morgan-Monroe State Forest near Martinsville. Teachers will stay in the Training Center, sharing one of the 10 sleeping rooms. Meals will be provided.
– Carrie Tauscher, Acting Community and Urban Forestry State Coordinator
Please see link below to download additional information.
To RSVP, please email Project Learning Tree: pl*@****in.gov
-
Arbor Ranger EAB Crossword Puzzle
Arbor Rangers ™ EAB Crossword Challenge
If you like challenges, then this crossword puzzle is for you! See if you can complete it after printing it out and filling in the correct answers to the clues listed. The sheet also includes a word search puzzle.
Ready for the puzzle solution? EAB Crossword Puzzle Answers
-

Stop the Emerald Ash Borer!
Help stop the spread of Emerald Ash Borer! HOW? Well, one way is not to transport any firewood from quarantined locations to other locations (quarantined or not). If you have a fireplace or fire pit, only use local wood. If you plan on having a bonfire, or barbequing at a picnic site away from home or camping, etc. make sure you don’t take firewood with you, but instead buy it from someplace in or near where you plan to burn it. Use up all the firewood too and don’t transport it back home or to another location.
How bad is the situation?
According to the Northern Research Station of the USDA Forest Service, ash trees affected by EAB requiring treatment, removal, or replacement number more than 17 million at an estimated cost of $10.7 billion and their spread continues to threaten Midwest states! Check out the latest infestation data on INDIANA EMERALD ASH BORER (EAB) QUARANTINE MAP posted by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources.
We are calling on YOU to help join us in slowing down this devastating pest! THANK YOU!
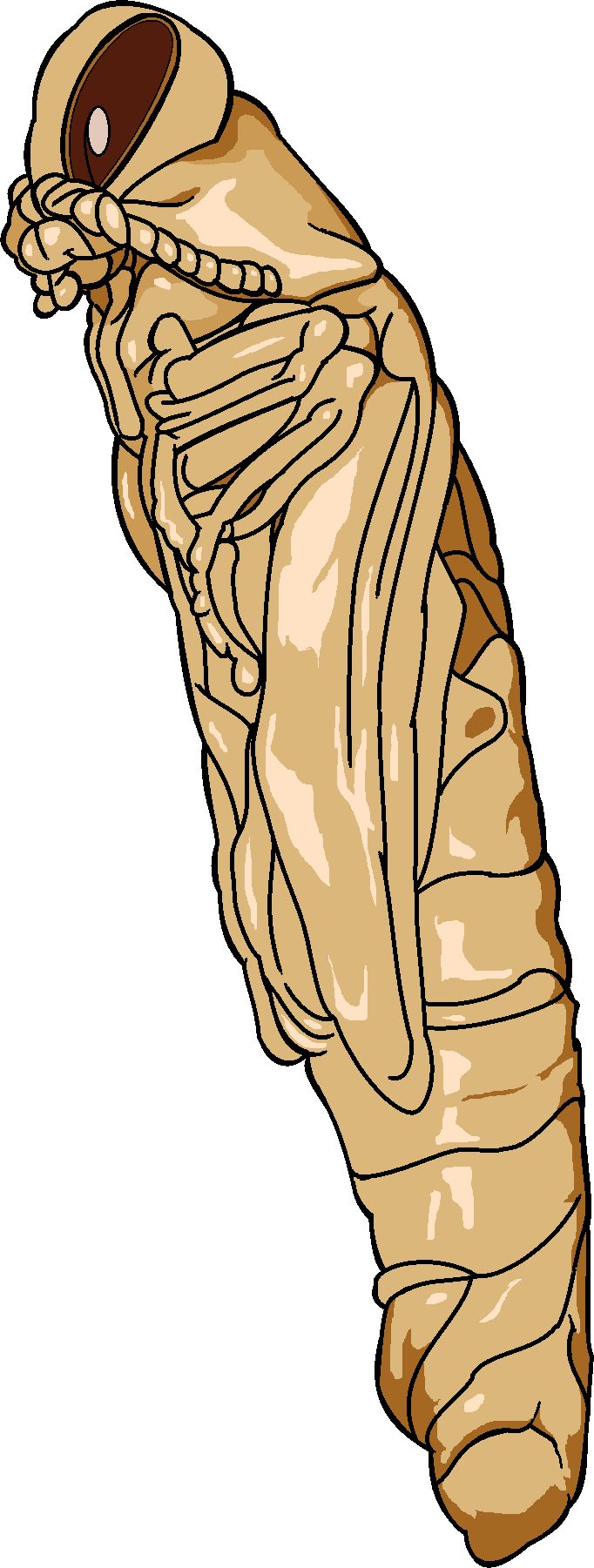
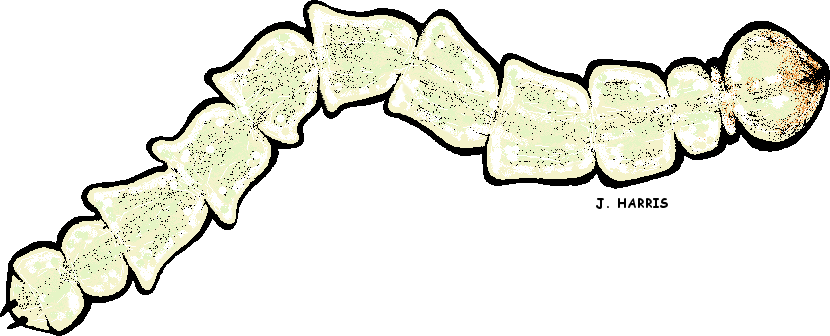
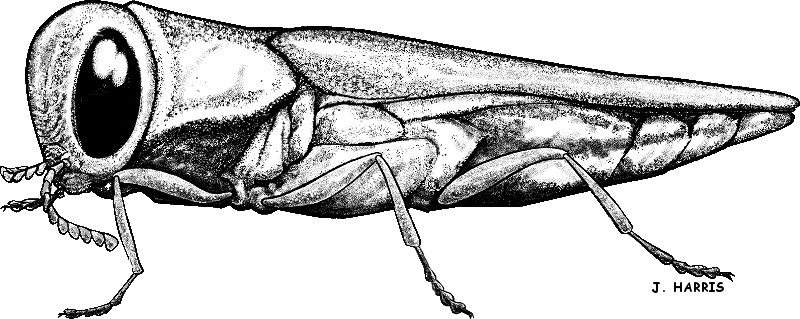
Emerald Ash Borer pupa by J. Harris For more information on Emerald Ash Borers (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) and what to do if you suspect an infestation in your Ash trees (Fraxinus spp.), check out these links below:
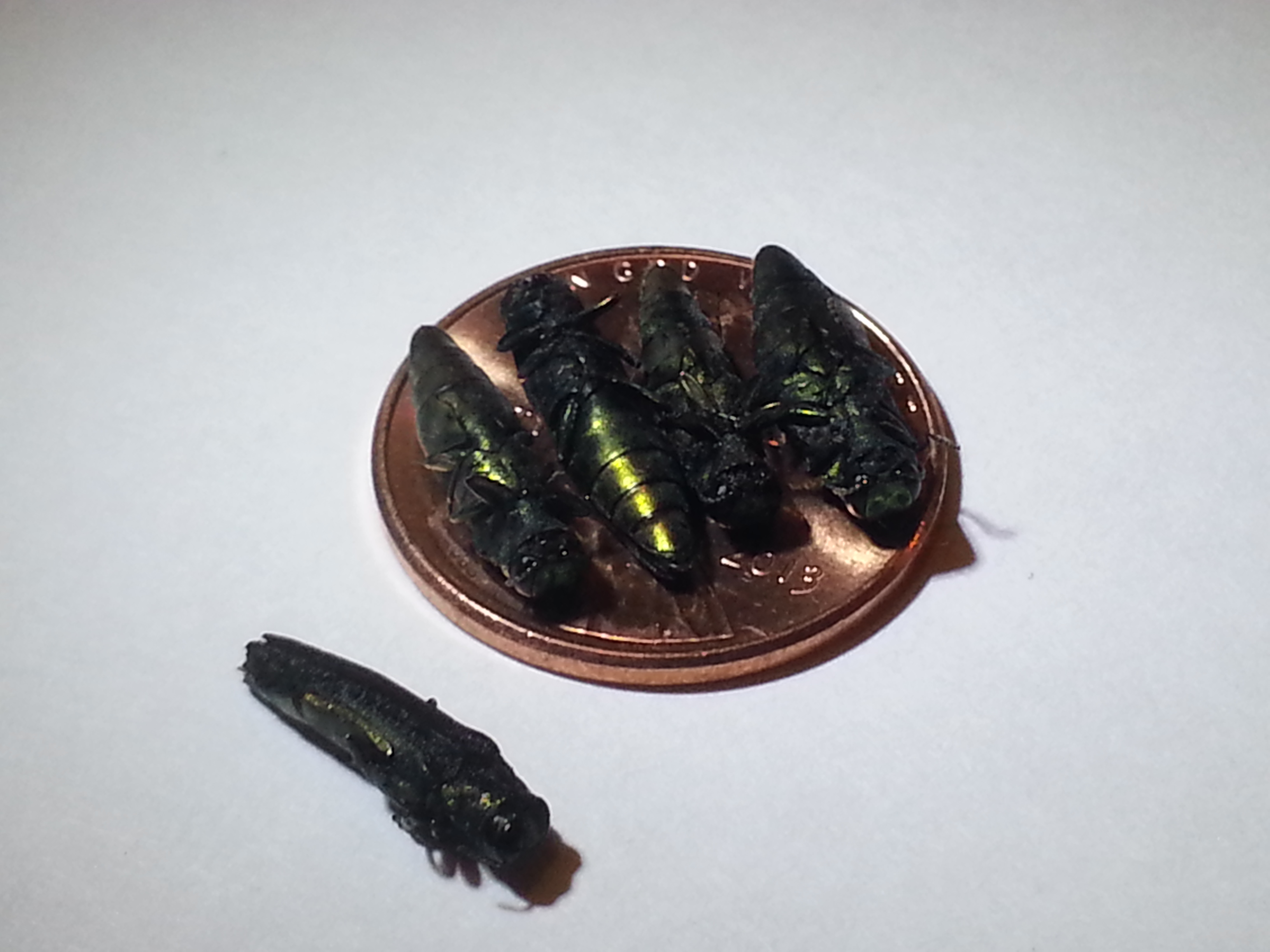

Four Emerald Ash Borers fit onto a penny. Photo by Jeff Harris, Arbor Rangers, LLC